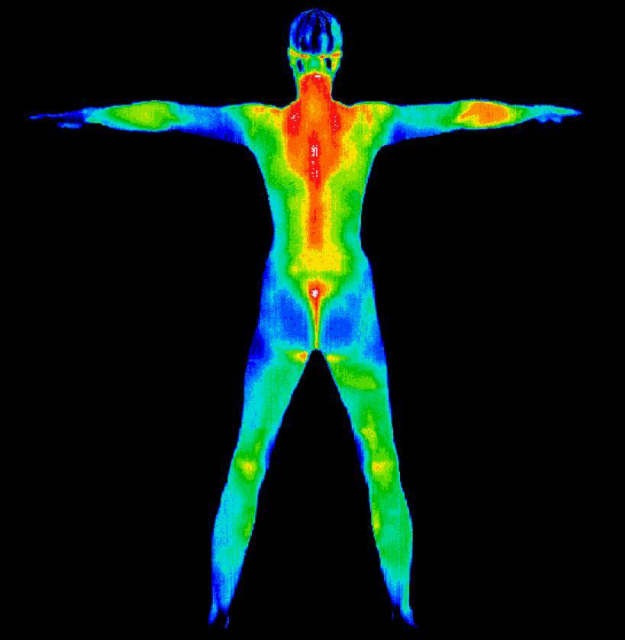
Raynaud sy.
– a non-invasive imaging diagnostic method, recording the real-time temperature patterns and temperature asymmetries at various locations on a body, helping thus to differentiate pathological processes of many diseases, pre-pathological conditions before the morphological changes and lesions (damage) appear in tissues of the musculoskeletal system.
In healthy people, heat distribution over the body surface is stabile and characteristic for each individual, just like a fingerprint. Every deviation from a physiological temperature pattern or temperature asymmetries indicate pathological changes, damage.
It represents:
- superficial organs: breast, thyroid, external genitals, superficial venous system
- individual locations of the locomotor system: shoulders, arms, spine, SI joints, joints of ankle, knee, thighs, tibia, face, head, neck, chest, abdominal wall
Identifiable diagnoses:
- Diseases with painful demonstrations: identification of the pain cause, including inflammation, neurological damage, necrosis, ischemia, or cancerogenic and neoplastic angiogenesis, myofascial pain syndrome
- Damage to muscles, tendons, ruptures of articular capsule, dislocations, sprains, ruptures
- Functional joint blockage: differentiation between mechanical cause and ligament damage
- Vasomotor headache, atypical facial pain
- Neuropathies in diabetic patients and threat of ulcerations
- Entrapment neuropathies: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Thoracic Outlet Syndrome – TOS, etc.
- Vasospastic Raynaud sy.
- Venous insufficiencies
- Arthritis of various types and origins (rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis urica (DNA)
- Monitoring of efficiency of therapeutic interventions
- Cysts, fibrous tissue parts, mastitis, dysplasia, breast tumours.
Thermography breast examination
Thermography breast examination facilitates the identification of
- cysts
- fibrosis
- mastitis
- dysplasia
- breast tumours
It is used to identify the status of breast tissues in women of all age categories, with all breast sizes, in pregnant women, and women with breast implants.
Asymmetric areas (i.e. with the difference of 1 degree of Celsius) indicate, with high probability, a present pathology. Thermography can identify a cluster of approximately 256 cancer cells, while a mammography can only detect cancer when a cluster of approximately 4 billion cells is formed. It is estimated that thermography can detect a cancer formation approximately 6 years sooner than with mammography.
Female breasts usually do not radiate a lot of heat. If they are healthy, a thermography image shows light-blue tones. They indicate low temperatures. However, red, orange, or yellow spots can indicate the presence of pathology and should be analysed in more details. Long-term studies showed the average sensitivity and specificity at the level of 90%. The results show that a persisting abnormal thermogram indicates a 22-fold higher risk of breast cancer.
Method:
A modern method of infrared thermography, detecting infrared radiation from a body surface in form of an image recording. The SVIT thermal imaging system holds the record in the thermal sensitivity among conventional medical thermal imaging systems – the standard deviation of the noise in the normal operation mode of the device with majority of matrix elements corresponds to the temperature of approximately 0.025 °C.
Principle:
Contactless scanning of thermal radiation produced by human heat, visualised and diagnosed using the SVIT, a special thermograph camera
Advantages:
- absolute harmlessness
- high sensitivity – high-quality interpretability
- regarded as the primary examination method, surpassing all other examination methods – active (e.g. ultrasound), or invasive
- without contraindications, except for undisciplined patients who do not comply with the requirements prior to the examination
- monitoring the therapy efficiency
Preparation for an examination:
24 hours prior to the examination, the use of all steroids, sympathicus-blocking agents, vasodilatation mediators, opiates, and transdermal patches must be discontinued
12 hours prior to the examination, the acupuncture, myoskeletal techniques, physical therapy, and electrodiagnostic tests must be avoided
6 hours prior to the examination, do not use ointments, creams, bandages, splints
3 hours prior to the examination, do not eat, drink, use medications
In the morning of the examination day, a client should take a shower, the skin must be clean, without creams, deodorants, and make-up.
Examples of diagnostics, pathology:
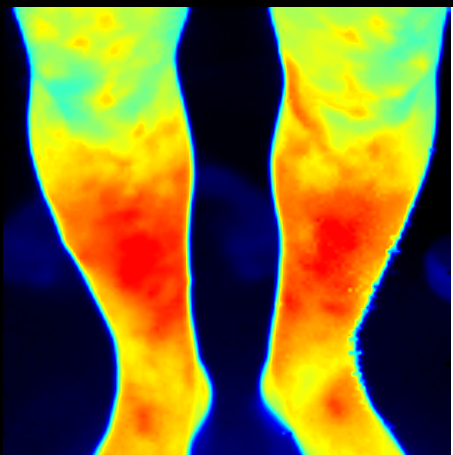
Client with DM II. – risk of ulcerous changes (tibial ulcers)
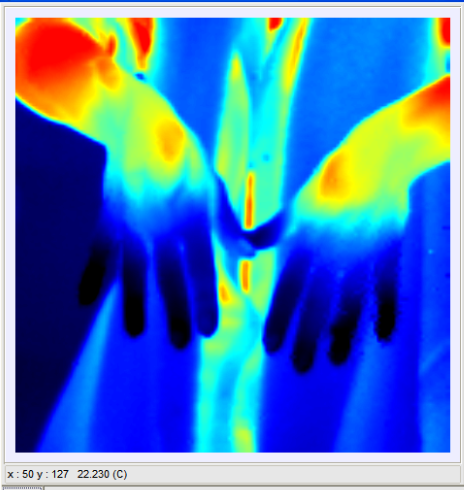

Raynaud sy.
Author: Mgr. Mrenková Lucia